2020年InForSec“走进蚂蚁集团”网络空间安全大学生夏令营活动计划于7月18日至19日在杭州举行;活动面向全国计算机、网络空间安全相关专业的本科生和在读研究生,旨在促进网络安全相关方向老师、学生之间的了解和沟通,帮助学生了解网络安全相关的研究方向。
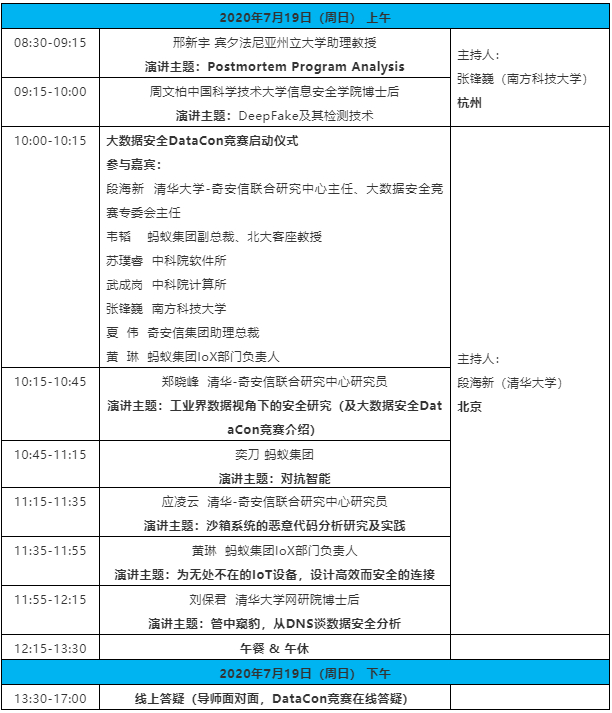
日程安排


请有意向参与夏令营活动并联系相应的导师的同学访问https://www.inforsec.org/wp/?p=3966,下载并提交相关资料。活动快捷报名,请点击并识别正文下方二维码。报名截止日期:2020年7月5日。

演讲嘉宾

纪守领
浙江大学研究员
演讲主题:Revisited Deep Learning Security: Empirical Analysis and Robustness Quantification
导师介绍:
纪守领获佐治亚理工学院电子与计算机工程博士学位、佐治亚州立大学计算机科学博士学位,现任浙江大学“百人计划”研究员、博士生导师,兼任佐治亚理工学院Research Faculty。主要研究方向为人工智能安全、数据驱动安全、软件与系统安全、大数据分析,发表论文100余篇。曾获中国国家优秀留学生奖、七项最佳论文奖、GSU杰出研究奖等。
内容摘要:
Deep learning security has drawn significant attention from the academia. Various kinds of attacks and defenses spring up like bamboo shoots. Given this, two interesting questions have raised: (1) what is the performance of the attacks against real world systems? and (2) how to understand/quantify the security space of deep models? Towards this, we recently revisited the transferability of adversarial examples against real world systems and studied the robustness for DNNs. In this talk, I will introduce some interesting results from these two perspectives.

林志强
俄亥俄州立大学副教授
演讲主题:Unveiling IoT Security from Bluetooth Low Energy
导师介绍:
Dr. Zhiqiang Lin is an Associate Professor of Computer Science and Engineering at The Ohio State University (OSU). He is also a faculty member at Translational Data Analytics Institute (TDAI), Center for Automotive Research (CAR), and the recently launched Institute for Cybersecurity and Digital Trust (ICDT) at OSU. His primary research interests are trusted computing, systems and software security, with an emphasis on developing automated program analysis and reverse engineering techniques and applying them to secure both the application programs including mobile apps and the underlying system software such as OS kernels and hypervisors. Dr. Lin is a recipient of both NSF CAREER award and AFOSR Young Investigator award.
内容摘要:
Being an easy-to-deploy and cost-effective low power wireless solution, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has been used by billions of Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices for various applications in many areas such as transportation, healthcare (e.g., recently on COVID19 contact tracing), wearables, retail, and smart homes. However, numerous vulnerabilities have also been identified in BLE IoT. In this talk, Dr. Lin will talk about a line of recent research from his group on BLE IoT security. In particular, he will first about the internals of how BLE IoT works including the corresponding protocols, then talk about the various flaws in BLE stacks from the protocol specification, to the design and implementation at the operating systems and applications, and finally he will talk about future works in this direction.

刘烃
西安交通大学网络空间安全学院副院长、教授
演讲主题:智能软件工程
导师介绍:
刘烃,博士,教授,西安交通大学网络空间安全学院副院长。主要研究方向包括软件工程和信息物理融合系统。2003年和2010年分别获西安交通大学学士和博士学位;2016-2017年美国康奈尔大学访问教授。获得2017年国家科技进步二等奖、以及2015年教育部科技进步一等奖等省部级科技奖励5项。在IEEE TIFS、IEEE TSG、IEEE TSE等国际权威期刊和ICSE、FSE、ASE、ISSTA、INFOCOM等国际顶级会议上发表论文70余篇,获得2019 IEEE INFOCOM、2016 IEEE ISSRE等会议最佳论文奖。
内容摘要:
代码自动生成和维护是软件工程领域历史最悠久和最受关注的方向之一。近年来,快速发展的人工智能技术使得机器对代码和人类需求的理解能力得到显著提升,为代码自动生成和维护提供了新的思路。本报告以自然语言理解驱动的软件自动生成和维护为例,探讨人工智能技术在软件工程领域的应用。

梁振凯
新加坡国立大学副教授
演讲题目:理解系统执行环境中的灵活度与安全问题
导师介绍:
Dr. LIANG Zhenkai is an Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science at National University of Singapore. He is also a co-Lead Principal Investigator of National Security R&D Lab of Singapore. His research interests are in system and software security, such as binary program analysis, security in Web, mobile, and Internet-of-things (IoT) platforms. He has been publishing high-impact papers in top security and software engineering conferences, and has won seven best paper awards, including Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC), USENIX Security Symposium, and ACM SIGSOFT Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE). He has been actively served as technical committee members and editorial board members of top security conferences and journals, including ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS), USENIX Security Symposium, Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), and IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing (TDSC). He is also a member of the Steering Group of NDSS. He has won the Annual Teaching Excellence Award of NUS in 2014 and 2015. He received his Ph.D. degree in Computer Science from Stony Brook University in 2006, and B.S. degrees in Computer Science and Economics from Peking University in 1999.

张锋巍
南方科技大学副教授
演讲主题:Using Hardware Features for (In)Security on Arm
导师介绍:
张锋巍老师是南方科技学计算机科学与工程系副教授,研究员。在加入南科大之前,他是美国韦恩州立大学计算机系助理教授,计算机和系统安全实验室的主任(2015-2019)。他于2015年获得美国乔治梅森大学计算机专业的博士学位。主要研究领域是系统安全,包括可信执行(trustworthy execution)、硬件辅助安全(hardware-assisted security)、恶意软件透明分析(transparent malware debugging)、交通安全(transportation security),以及可否认加密(plausible deniability encryption)。张老师已经发表了40余篇国际会议和期刊论文,包括IEEE S&P, USENIX Security, NDSS, IEEE TIFS和IEEE TDSC。张老师是多个国际顶级会议程序委员会的成员,包括IEEE S&P,ACM CCS,ACSAC,IEEE/IFIP DSN等。张老师是ACSAC 2017年杰出论文奖的获得者和入选IEEE/IFIP DSN 2020最佳论文提名。他的研究工作曾获得了多项美国自然基金项目的支持。
内容摘要:
Processors nowadays are consistently equipped with debugging features to facilitate the program debugging and analysis. Although the debugging architecture has been presented for years, the security of the debugging features is under-examined since it normally requires physical access to use these features in the traditional debugging model. Arm introduces a new debugging model that requires no physical access since Armv7. In this new debugging model, a host processor is able to pause and debug another target processor on the same chip (inter-processor debugging). The idea of Nailgun attack is to misuse the debugging architecture with the inter-processor debugging since recent Arm systems allow the debug host to pause and debug the target even when the target owns a higher privilege. Our experiments discover a number of vulnerable devices including IoT devices like Raspberry PI, all commercial Arm-based cloud platforms, and mobile phones from Huawei, Motorola, and Xiaomi. For further verification, we show that Nailgun attack can be used to access the Secure Configuration Register (which is only accessible in the secure state) on Raspberry PI and extract the fingerprint image stored in the secure memory of a mobile phone with a non-secure kernel module.

钱志云
加州大学河滨分校副教授
演讲主题:SymTCP: Eluding Stateful Deep Packet Inspection with Automated Discrepancy Discovery
导师介绍:
Zhiyun Qian is the Everett and Imogene Ross associate professor in the CSE department at the University of California Riverside. He is a recipient of the NSF CAREER Award for 2017. His main research interests are in the area of system and network security, including vulnerability discovery, side channel analysis, applied program analysis, system building, and measurement of real-world security problems. He is a recipient of the NSF CAREER Award in 2017, Applied Networking Research Prize from IRTF in 2019, Facebook Internet
Defense Prize Finalist in 2016, and the most creative idea award from Geekpwn 2016.
内容摘要:
A key characteristic of commonly deployed deep packet inspection (DPI) systems is that they implement a simplified state machine of the network stack that often differs from that of endhosts. The discrepancies between the two state machines have been exploited to bypass such DPI based middleboxes. However, most prior approaches to do so rely on manually crafted adversarial packets, which not only are labor-intensive but may not work well across a plurality of DPI-based middleboxes. Our goal in this work is to develop an automated way to craft candidate adversarial packets, targeting TCP implementations in particular. Our approach to achieving this goal hinges on the key insight that while the TCP state machines of DPI implementations are obscure, those of the endhosts are well established. To this end, we develop a system called SYMTCP to systematically explore the TCP implementation of an endhost, identifying candidate packets that can reach critical points in the code (e.g., which causes the packets to be accepted or dropped/ignored); such automatically identified packets are then fed through the DPI middlebox to determine if a discrepancy is induced and the middlebox can be eluded. The results are promising as it discovered novel evasion strategies that are not previously reported (e.g., involving the urgent pointer).

杨珉
复旦大学计算机学院副院长,教授
演讲主题:面向AI系统的安全问题研究
导师介绍:
杨珉,国家973项目首席科学家,教育部青年长江特聘教授,复旦大学计算机学院教授、博士生导师。现任中国网络空间安全协会理事,国家网络空间安全重点专项终评专家、国家自然科学基金终评专家、教育部重点实验室评估组专家等学术兼职。
主研领域为网络空间安全,在国内率先开展移动安全问题研究,形成较大的社会和学术影响力,研究发现曾得到多位国家领导人的多次批示。曾荣获上海市IT青年十大新锐、上海市青年五四奖章、上海市十大杰出青年提名奖等荣誉称号。

程光
东南大学网络空间安全学院院长、教授
演讲主题:加密网络流量测量和分析
导师介绍:
程光,东南大学教授、博导,现任东南大学网络空间安全学院执行院长,计算机网络和信息集成教育部重点实验室主任、国家网络空间国际治理研究基地(东南大学)执行主任、江苏省网络空间安全高校联盟理事长、中国指挥控制学会网络空间安全专委会副主任、信息系统安全国防实验室学术委员会委员等社会兼职。
2003年获东南大学工学博士,2006年-2007年在美国佐治亚理工大学从事博士后研究,2012年和2016年期间分别在美国亚利桑那大学和美国德州奥斯汀分校从事高级访问学者研究工作。2017年被中央网信办评为 “网络安全优秀教师”,入选江苏省“青蓝工程”、“333工程”、“六大人才高峰”、“华英青年学者”、“华英学者”。主持中央网信办、教育部的“一流网络安全学院建设示范项目”、“网络空间国际治理研究基地”、教育部网络空间安全新工科等项目。2018年获得国家教学成果一等奖,2014年获得江苏省科学技术奖二等奖等。
研究方向为在网络空间安全、流量大数据、未来网络理论与方法等研究领域承担国家省部级科研项目30项。在国内外顶级会议和期刊如IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking、计算机学报、软件学报等发表学术论文100余篇,发表SCI索引论文近20篇,出版专著6部。获得国家、省部级和企业科研项目资助30余项,取得了创新性研究成果;获得授权发明专利22项,已经成功转化5项专利。出版专著7部,培养研究生100余人。

武成岗
中科院计算所教授级高工
演讲主题:一种基于SMAP的安全高效的进程内隔离方法
导师介绍:
武成岗,中国科学院计算技术研究所研究员级高工,博士生导师。2001年于中国科学院计算技术研究所获博士学位。长期从事基于编译技术的软件安全技术的研究,旨在通过程序分析技术,增强软件的安全性、可靠性和高效性。在程序缺陷定位、二进制代码的分析变换及优化、运行时程序行为监测、安全防御等方面,有着较深的技术积累。发表论文30余篇,部分发表在TSE、ICSE、ASE、TPDS、TACO、SIGMETRICS、PACT、CGO、VEE、DATE等学术会议和期刊上,获得授权专利16项,软件著作权5项,并于2012年荣获北京市科学技术二等奖。担任国际学术会议CGO 2013大会主席、APPT 2013程序委员会主席,还担任CGO2015-2018、PPoPP2017-2018、PLDI2012、CCGrid 2015、ICPADS 2014、PPPJ2014等会议的程序委员会委员。

张阳
德国CISPA研究中心研究员、博士
演讲主题:Privacy in the Era of Machine Learning
导师介绍:
Yang Zhang is a faculty member at CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security, Germany. Previously, he was a group leader at CISPA. He obtained his Ph.D. degree from University of Luxembourg in November 2016 under the supervision of Prof. Sjouke Mauw and Dr. Jun Pang. Yang’s research interests lie at the intersection of privacy and machine learning. Over the years, he has published multiple papers at top venues in computer science, including WWW, CCS, NDSS, USENIX Security, and IJCAI. His work has received NDSS 2019 distinguished paper award. Yang has served in the technical program committee of ACM CCS 2020 2019, ISMB 2019, WWW 2020, RAID 2020, ICWSM 2020, and PETS 2021 2020.
内容摘要:
The past decade has witnessed the fast development of machine learning techniques, and the key factor that drives the current progress is the unprecedented large-scale data. On the one hand, machine learning and big data can help improve various domains of people’s life quality. On the other hand, they can also cause severe risks to people’s privacy. In this talk, I will present our research on the intersection of data privacy and machine learning. First, I will show how to use machine learning techniques to assess and mitigate privacy risks for various types of data, including social network data, location data, and biomedical data. Then, I will present our research on quantifying privacy risks caused by machine learning models. In particular, I will discuss our newest results on membership inference and data reconstruction.

段海新
清华大学网研院教授
演讲主题:互联网基础设施安全的依赖性分析
导师介绍:
段海新,清华大学网络科学与网络空间研究院教授,网络空间安全实验室主任,博士生导师。近20年来一直工作在网络安全科研和教学第一线。作为课题负责人承担国家自然科学基金、973、863等多项课题,在网络和系统安全国际顶级学术会议(Security&Privacy、USENIX Security、CCS、NDSS等)上发表多篇论文,并获NDSS 2016年“杰出论文奖”。兼任中国网络空间安全协会理事、密码学会协议安全专委会委员、互联网协会安全工作委员会委员等职务,是多个国际会议程序委员和国际期刊审稿人。
段海新带领团队发现了互联网协议中域名系统、内容分发网络和Web协议等若干重大安全漏洞并提出了解决方案,促进了产品和标准的更新,产生了重要的国际影响;他长期从事互联网安全检测与应急响应,检测黑色产业、打击网络犯罪,为国家网络安全做出了重要贡献;他从事网络安全教学十多年,注重培养学生的实践和创新能力,作为联合创始人的“蓝莲花战队”多次在国际著名的网络安全竞赛中名列前茅,作为联合发起人组织网络安全研究国际学术论坛InForSec和全国网络安全对抗联赛XCTF,对我国网络安全人才培养发挥了重要作用。2016年获得中央网信办颁发的“网络安全优秀人才”奖。

邢新宇
宾夕法尼亚州立大学助理教授
演讲主题:Postmortem Program Analysis
导师介绍:
Dr. Xinyu Xing is an Assistant Professor at Pennsylvania State University. His research interests include exploring, designing and developing new techniques to automate vulnerability discovery, failure reproduction, vulnerability diagnosis (and triage), exploit and security patch generation. His past research has been featured by many mainstream media and received the best paper awards from ACM CCS and ACSAC. Going beyond academic research, he also actively participates and hosts many world-class cybersecurity competitions (such as HITB and XCTF) and frequently shared thoughts at prestigious industrial conferences (such as Black Hat and DEFCON).
内容摘要:
Despite the best efforts of developers, software inevitably contains flaws that may be leveraged as security vulnerabilities. Modern operating systems integrate various security mechanisms to prevent software faults from being exploited. To bypass these defenses and hijack program execution, an attacker needs to constantly mutate an exploit and make many attempts. While in their attempts, the exploit triggers a security vulnerability and makes the running process abnormally terminate.
After a program has crashed and abnormally terminated, it typically leaves behind a snapshot of its crashing state in the form of a core dump. While a core dump carries a large amount of information, which has long been used for software debugging, it barely serves as informative debugging aids in locating software faults, particularly memory corruption vulnerabilities. As such, previous research mainly seeks fully reproducible execution tracing to identify software vulnerabilities in crashes. However, such techniques are usually impractical for complex programs. Even for simple programs, the overhead of fully reproducible tracing may only be acceptable at the time of in-house testing.
In this talk, I will discuss how we tackle this issue by bridging program analysis with artificial intelligence (AI). More specifically, I will first talk about the history of postmortem program analysis, characterizing and disclosing their limitations. Second, I will introduce how we design a new reverse-execution approach for postmortem program analysis. Third, I will discuss how we integrate AI into our reverse-execution method to escalate its analysis efficiency and accuracy. Last but not least, as part of this talk, I will demonstrate the effectiveness of this AI-assisted postmortem program analysis framework by using massive amounts of real-world programs.

周文柏
中国科学技术大学博士后
演讲主题:Deepfake及其检测技术
嘉宾介绍:
周文柏,中国科学技术大学网络空间安全学院,博士后研究员,图象图形学学会多媒体取证与安全专家委员会委员,中国科学技术大学“墨子杰出青年”获得者。2019年博士毕业于中国科学技术大学,主要研究兴趣包括信息隐藏与人工智能安全。在TIFS、TCSVT、ICCV、AAAI等国际知名期刊和会议上发表高水平学术论文十余篇,中国科技大学网IPC人工智能安全战队队长,曾获Facebook Deepfake Detection Challenge(DFDC)全球第二,IJCAI-19-阿里巴巴人工智能对抗算法竞赛第一,2018 CAAD对抗样本攻防赛六强。主持安徽省自然科学基金1项。
内容摘要:
Deepfake“深度换脸”是近期新兴的热点问题,通过人工智能技术,实现人脸视频的模拟与伪造。与传统的基于计算机图形学的高门槛换脸技术不同,Deepfake得益于AI技术的飞速发展,大大降低了换脸手段的技术门槛。这类技术目前已被广泛用于娱乐应用中,并开发了如ZAO、Impressions等换脸软件。而Deepfake本身亦是一把“双刃剑”,这类技术的盛行带来了极大的潜在风险,尤其是在政治、金融、公共安全等领域,一旦出现恶意伪造,如身份伪造、舆情煽动等,都将对国家和社会带来巨大危害,因此各国政府与诸多国际机构高度关注Deepfake的防治。
Deepfake需要经历媒体数据获取、人脸分割、面部伪造、替换融合、伪造痕迹修复等主要过程,最终实现深度换脸,这也意味着Deepfake的检测将是复杂而全方位的工作。本报告将从现有技术与实际应用场景出发,围绕团队在生成方面的相关工作和DFDC比赛中的解决方案,给出对于Deepfake及其检测技术的一些探究与思考。

郑晓峰
清华-奇安信联合研究中心研究员
演讲主题:工业界数据视角下的安全研究(及DataCon竞赛介绍)
嘉宾介绍:
郑晓峰 奇安信集团技术研究院研究员,清华大学-奇安信联合研究中心研究员,羲和网络安全实验室主任。从事网络基础设施、基础协议安全相关研究,研究成果发表在网络安全国际顶级学术会议USENIX Security、NDSS,并获DNSS 2016年“杰出论文奖”。曾获Google浏览器安全计划奖励、GeekPwn(2015)46万元奖励、GeekPwn(2018)25万元奖励、GeekPwn(2019)15万元奖励、TSRC通用软件漏洞10万元奖励等荣誉。研究成果帮助许多世界知名的互联网企业修复了安全漏洞,如Bank of America、Google、Facebook、Mozilla、Apple、Amazon、中国建行、中国银联、支付宝等,推动了Google公司修正Chrome,促进了国际互联网标准组织IETF修改相关国际标准。

应凌云
清华-奇安信联合研究中心研究员
演讲主题:沙箱系统的恶意代码分析研究及实践
嘉宾介绍:
应凌云,奇安信集团技术研究院研究员,清华大学-奇安信联合研究中心研究员,中国科学院大学岗位教授,硕士生导师。长期从事网络安全相关技术研究工作,已发表学术论文29篇,出版合著1部,主持国家自然科学基金、国家发改委信息安全专项、北京市自然科学基金等项目15项,申请技术发明专利15项,参与国际标准提案2项、国家行业标准编制4项,先后荣获中国通信学会科学技术奖(科技进步类)一等奖(2018)、北京市科学技术奖二等奖(2017)、中国电力技术发明奖三等奖(2017)等奖项荣誉。

刘保君
清华大学博士后
演讲主题:管中窥豹,从DNS谈数据安全分析
嘉宾介绍:
刘保君是清华大学网络空间与网络科学研究院博士后,2018年于伯克利国际计算机科学研究所访问。主要研究方向为网络基础设施安全。博士期间学术论文发表于IEEE S&P、USENIX Security、CCS、NDSS、IMC等国际网络安全领域重要会议,获得清华大学博士生国家奖学金、NDSS 2019最佳论文奖,IMC 2019最佳论文奖与安全社区贡献奖提名。








